“It should be on the menu of options that California has. Is it going to be the number one option? Definitely not.”
So far, its use has been limited in California. Pacific Gas and Electric has a pilot program — the first in the nation — that lets up to 1,000 residential customers with bidirectional chargers sell power back to the utility. Some school districts also are experimenting with it.
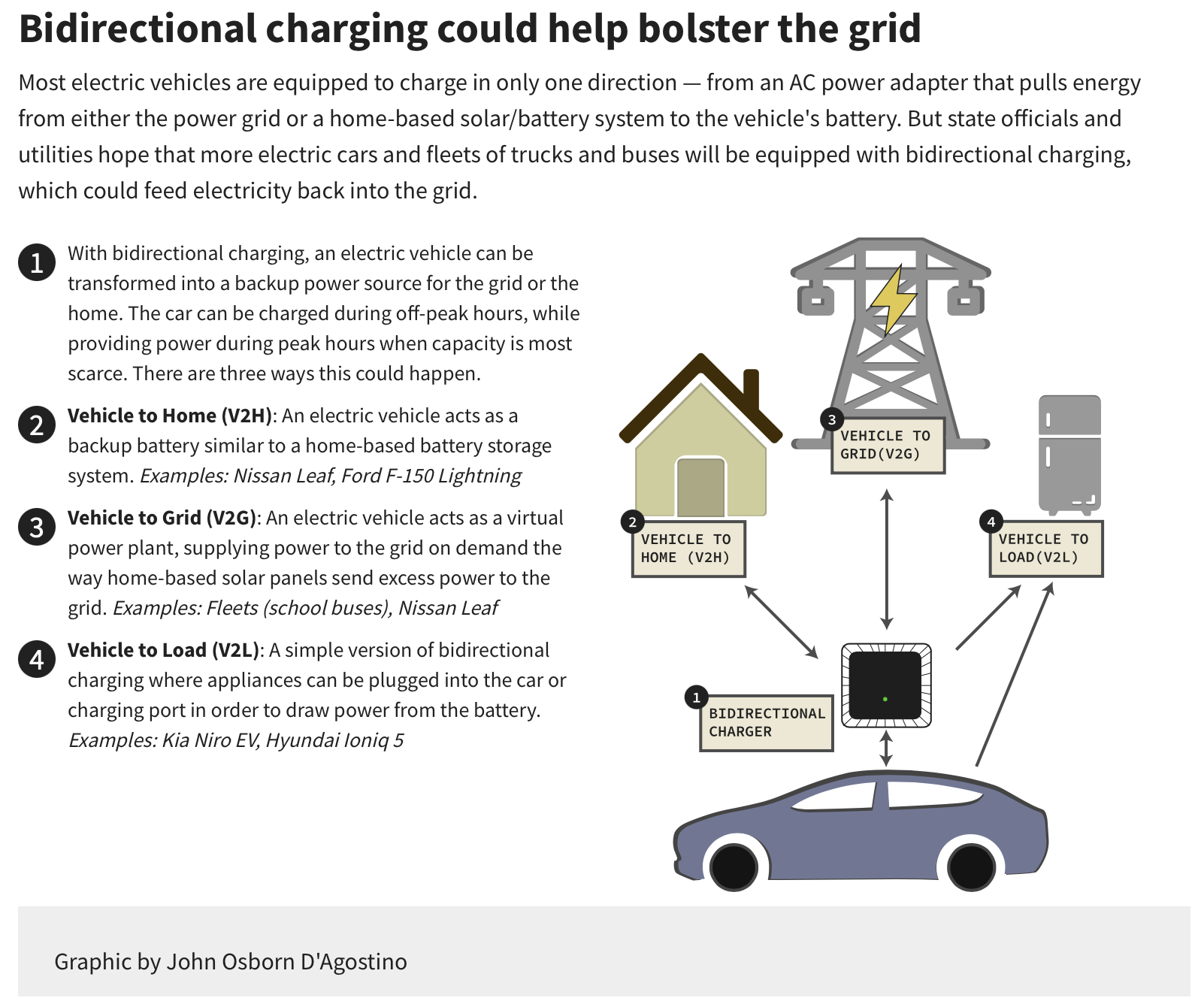
Only about half a dozen electric car models currently are equipped with bidirectional capabilities, including the Hyundai Ioniq 5, Nissan Leaf and Ford F-150 Lightning. Tesla announced recently that all its models will have it by 2025.
Electric vehicles convert one type of energy, alternating current electricity, into another, direct current, which is stored in a battery. Bidirectional charging means that an electric vehicle can convert the energy it has stored in its battery and send it to other sources, such as home appliances or back to the grid.
Willett M. Kempton, a University of Delaware professor who has studied bidirectional charging for more than two decades, said the vast majority of the time a vehicle is parked and not using electricity.
“Five percent of the time you’re using the car and you want to have enough energy — electricity or gasoline — to get to where you’re going and back. But most of the time, it’s just sitting there and some other use could be made of it,” he said.
Kempton said these vehicles, properly managed, could be sources of reserve energy, supplanting backup sources that burn fossil fuels.
Gregory Poilasne, co-founder and CEO of Nuvve Holding Corp., which sells electric fleet charging services, said a big challenge is that cars are unreliable energy assets. “At any time, somebody might come in and unplug the car,” he said. But he added, as the technology becomes more reliable and affordable, bidirectional cars and fleets should increase.
The cost: $3,700 per car
In Denmark, bidirectional charging earns electric vehicle fleet owners who sell power to the grid $3,000 per vehicle a year, Poilasne said, adding that this reduces the average total cost of electric car ownership by about 40%.
But citing the high cost, automakers oppose the Senate bill that would mandate the chargers for all new cars sold in California by 2030. It would increase the average cost of an electric car by $3,700, according to an opposition letter written by Curt Augustine of the Alliance for Automotive Innovation, which represents General Motors, Ford and other major auto companies.



