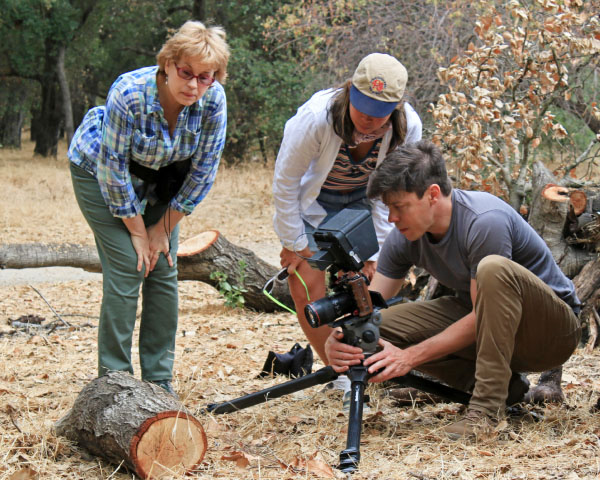
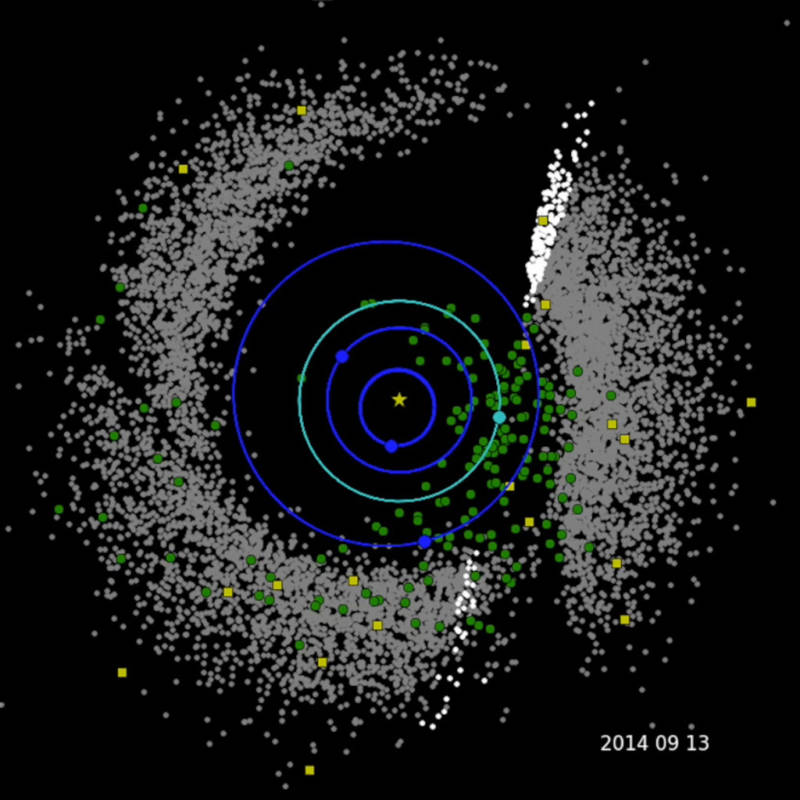
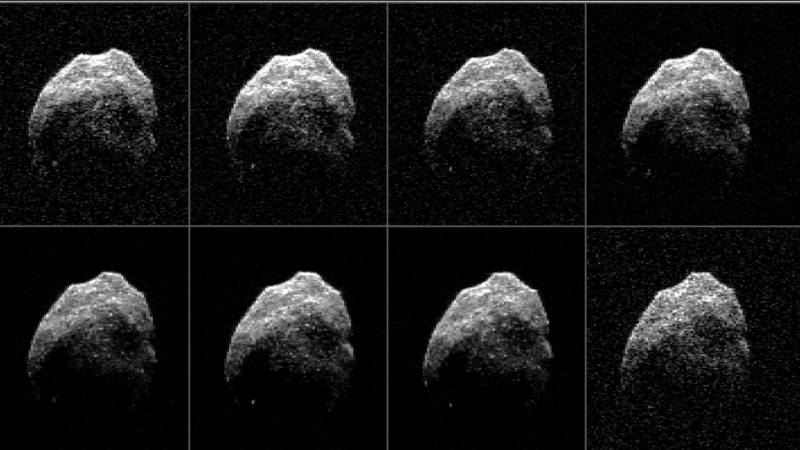
After a three-year mission hunting for near-Earth asteroids and comets, NASA’s NEOWISE program has delivered a fresh batch of discoveries. In the past year alone, NEOWISE has detected 97 previously unknown solar system objects, 28 of which are Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) that come close to or cross Earth’s orbit, and can pose a potential collision threat.
In the past three years, NEOWISE has revealed the characteristics of 693 Near-Earth Objects, 114 of which are new discoveries. In the past year alone, it discovered ten potentially hazardous objects. An object is classified as ‘potentially hazardous’ if its minimum distance from Earth is 4,647,790 miles — or less.
NEOWISE is a reinvention of NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission, which was launched back in December 2009. WISE’s goal was to map the entire sky with its 16-inch telescope looking for sources of infrared light, which it accomplished in six months of observation.
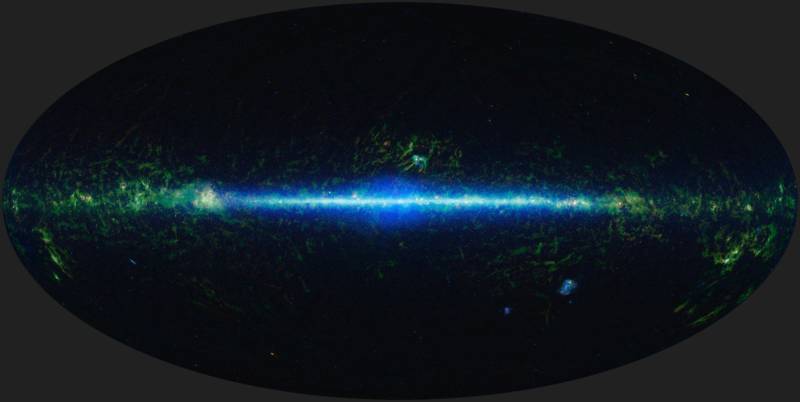

With extreme sensitivity to infrared radiation at four different wavelengths, WISE detected faint celestial heat sources across the cosmos — such as galaxies billions of light years away, objects within the Milky Way such as black holes, forming star systems and cool brown dwarf stars, and asteroids and comets within our solar system.
Just within our solar system WISE observed about 154,000 objects, including 33,500 new asteroid and comet discoveries.