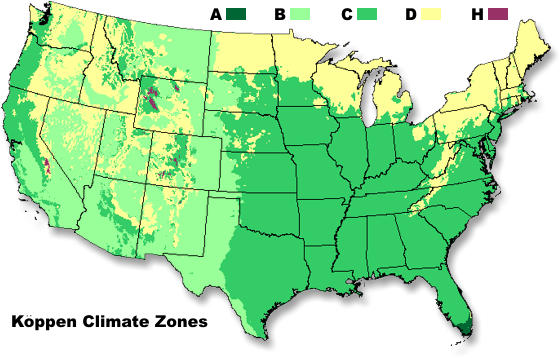
Check out this resource from NOAA to learn about the major climate zones in the continental United States.
There's a lot of talk about climate change in the news, but it's a topic that can be really hard to understand. What exactly is climate change? Put simply, climate change is a change in average weather patterns over a long period of time. However, people often confuse natural variations in weather with climate change. In order to understand the distinction, you have to understand the difference between weather and climate. Weather refers to atmospheric conditions like temperature, precipitation, and wind at a specific time and place, whereas climate refers to long-term trends of weather.
Look outside. Is it sunny? Is it raining? Is it snowing? Is it windy? Whatever is happening right now is weather. Weather varies from day to day. Some days it might be sunny, other days in might be cloudy and rainy.
A region’s climate is determined by weather patterns -- patterns in precipitation, temperature, humidity and wind -- usually averaged over a 30-year span. Climate gives us an idea of what the weather in a particular region might be. For example, if it’s winter in Miami, you don’t expect it to snow. That’s because Miami has a tropical climate with warm temperatures year-round and lots of rain. Likewise, if it's winter in Maine, you don't expect it to be 95 degrees Fahrenheit.
To determine changes in climate, you have to look at long-term trends and averages of past weather data. For example, past weather data from California's Central Valley shows that this area is experiencing warmer temperatures and less fog compared to what would be normal variations in weather. This suggests a changing climate.



