"The human body isn't designed to process this form of sugar at such high levels," Goran said in a statement. "Unlike glucose, which serves as fuel for the body, fructose is processed almost entirely in the liver where it is converted to fat, which increases risk for diabetes, cardiovascular disease and liver disease."
Goran's assertion is not universally accepted. Other health researchers, like Fred Brouns at Maastricht University in the Netherlands, say sugar is basically sugar. He has argued that we should spend less time fixating on fructose and its role in the emerging chronic disease epidemics, and more time looking at sugar and energy over-consumption overall.
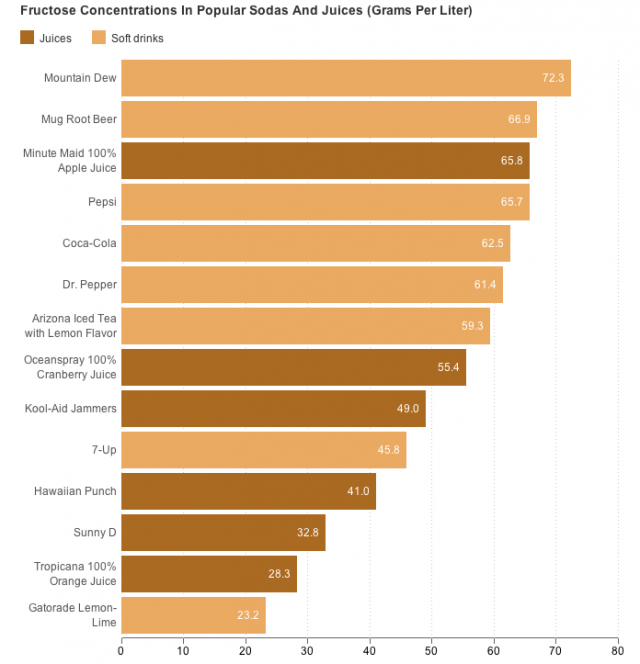
Goran says that while high fructose corn syrup in soda and food has become a focal point for researchers and public health advocates in recent years, there's been less attention on the link between fruit juice and obesity and diabetes.
"But it's hard to imagine why any there's reason why juices wouldn't be as harmful as sodas if they're delivering the same amount of sugar," he tells us.
One of the biggest problems, Goran notes, is that nutrition labels only tells us the total grams of sugar — so it's hard to know how much fructose is in any product. (The term "sugars" on the label can include sucrose, which is a combination of glucose and fructose; lactose and other variations.)
But, Goran adds, if we're getting fructose from whole fruit, that's a different story. The fructose in whole fruit comes with fiber, which slows down and reduces the absorption of the sugar in the body, "serving as a sort of antidote to the negative effects of fructose metabolism."
Barry Popkin, a leading obesity researcher and professor of nutrition at the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, agrees that fruit juice consumption is associated with health risks because of the high sugar content.
"Yes, from our long-term, huge studies in Singapore, Australia, the U.S. and Europe, I think 100 percent fruit juice is as bad as sugar-sweetened beverages for its effects on our health," he tells us. And, Popkin adds, every long term study on the effects of 100 percent fruit juice intake on diabetes risk shows a very significant risk, too.
Popkin notes that only about nine countries have banned fruit juices from schools. "However, all countries now say a maximum four ounces of fruit juice whereas 20 years ago we said unlimited," he adds.
So what's a juice lover to do with so many super-sweet products on the market? As NPR has reported, some beverage makers are now starting to cut the sugar. Goran recommends diluting juice you buy at the store with 50 percent water.
"From a public health perspective, we're going to need to change the cultural norms about how sweet things like juice really need to be," he says.