In a new push to stop further depletion of California’s shrinking aquifers, state regulators are turning to technology once used to count Soviet missile silos during the Cold War: satellites.
Satellites Are Becoming a Part of California's Water Conservation Strategy

Historically, California’s farmers could pump as much as they wanted from their wells. But as a consequence of that unrestricted use, the underground water table has sunk by hundreds of feet in some areas, and the state is now trying to stabilize those aquifers.
Regulators need to calculate just how much water each farmer is using across California’s vast agricultural lands, and scientists and private companies are now offering a technique that uses images from orbiting satellites.
“The days of agricultural anonymity are over,” says Joel Kimmelshue, co-founder of the company Land IQ, which is helping to hone the technique.
Water surveillance got a big boost when California passed a law in 2014 that aims to protect the state’s aquifers. It places limits on the amount of water that farmers are allowed to pump.
There was a big problem: Local officials like Eric Limas weren’t sure how to enforce limits on water use. Limas is general manager of the Lower Tule River and Pixley irrigation districts, in Tulare County, where aquifers are among the most depleted in the entire state. He’s also in charge of a newly established groundwater sustainability agency for that area.
“That was one of the first conversations that our groundwater committee tackled,” Limas says. “‘OK, how are we going to do that? Are we going to measure every molecule that’s pumped?'”

Limas doesn’t even know exactly how many wells there are in his part of the county. Thousands of them are hidden away in the middle of cornfields and almond orchards.
Many farmers weren’t inclined to help him out, especially in the first years after the law was passed. Limas recalls the initial reaction: “At first it’s like, ‘You’re crazy if you think you’re going to come on my place and … figure out how much I’m pumping. That’s my water.'”
Then Limas heard that researchers at California Polytechnic State University had developed a way to estimate the amount of water used by agricultural crops from images recorded by NASA-operated satellites.
Land IQ, meanwhile, was using that same technique — supplemented with stations on the ground — to collect data on field-by-field water use. It sounded like “Star Wars stuff,” Limas recalls. But it also sounded easier and cheaper than getting water meters installed on every well in his district.
The technique involves several steps. The first is figuring out which crops are growing on each field. The satellite images, which are updated almost every week, contain clues: the shade of green, the spacing of vegetation, the time of year the field turns green.
Combining these clues, Kimmelshue says, produces a fingerprint of each crop. “We have a fingerprint for walnuts and a fingerprint for alfalfa, tomatoes and all these different crops,” he says.
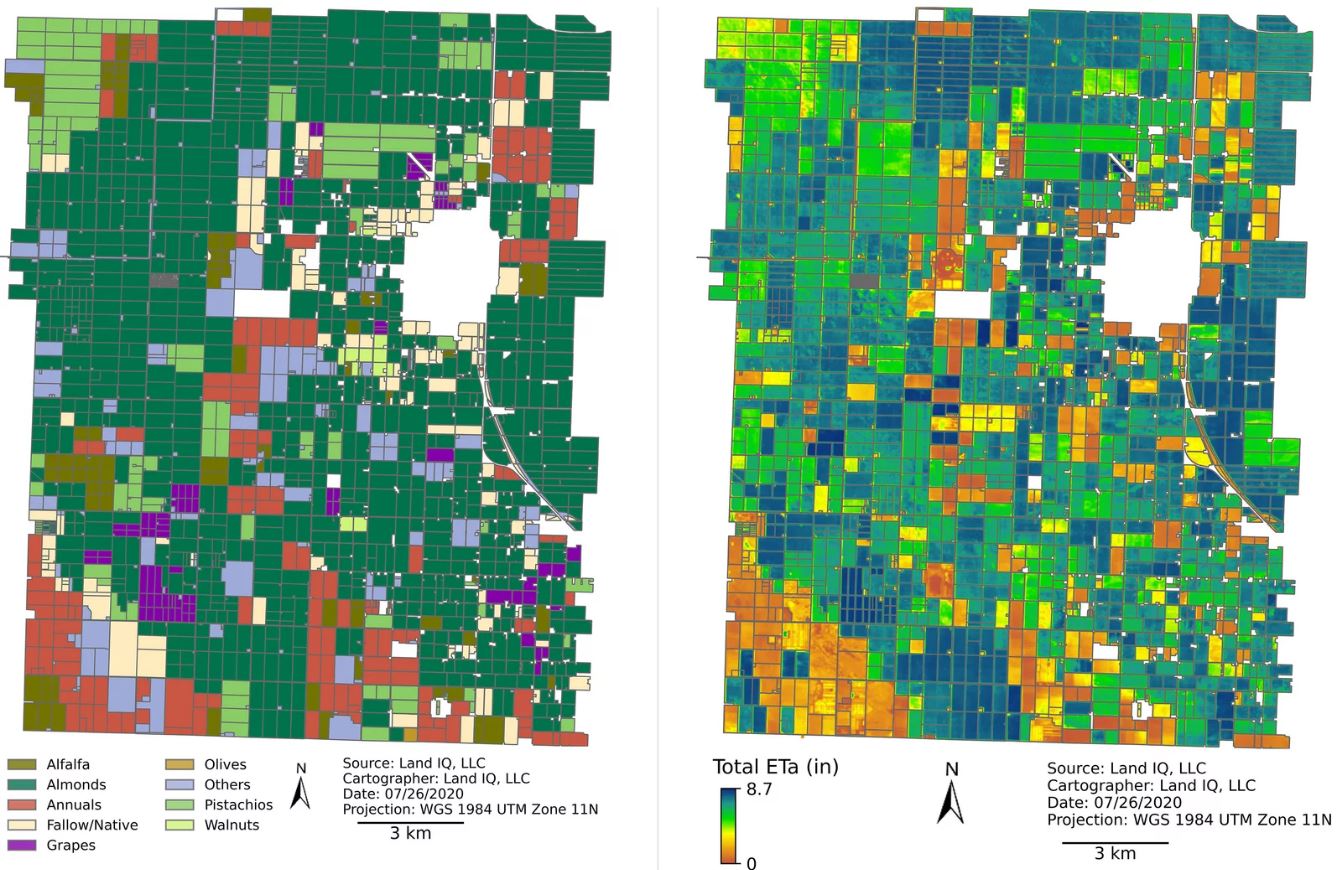
About 4% of the time, Kimmelshue says, there’s a case of mistaken identity. “We might confuse almonds for peaches,” he says. “But a peach tree and an almond tree have similar water needs” so the estimate of water use still ends up being quite accurate.
Each crop, at a particular point in its life cycle, takes up a predictable amount of water and releases it through its leaves, depending on local weather conditions.
Land IQ has set up local monitoring stations to keep track of things like wind speed, heat and humidity, at hundreds of locations. Putting it all together, the company calculates the amount of “evapotranspiration” — the amount of water that the plants are releasing to the air, as well as what’s evaporating from the soil.

That’s different from the amount that farmers are pumping because some irrigation water that’s pumped from the aquifer sinks back into the earth. Because of this, Kimmelshue has convinced officials like Limas that it’s more important to regulate water consumption, in the form of evapotranspiration, rather than water pumping.
He’s now selling that data to more than a dozen groundwater regulatory agencies, including the ones that Eric Limas manages.
Limas and his colleagues can monitor how much water is consumed by every farmer, field by field, and show farmers how that compares with their legal allotment under the new Sustainable Groundwater Management Act.
“A lot of guys are going in and looking at their water budgets and saying, ‘Oh, yeah, we don’t have enough water to plant that summer crop,'” Limas says.
That’s how the process is supposed to work. Farming practices are supposed to change to conserve aquifer water.
Some officials worry that it won’t go so smoothly when limits on groundwater use get tighter over the next two decades, while others are predicting court battles over whether the satellite-based technique is accurate. Some farmers say that regulators ultimately may shift to using data from water meters that are installed on every well.
In the meantime, though, the technique is growing more popular.
Later this week, a coalition of scientists, NASA and environmental groups like the Environmental Defense Fund plans to launch a new version of space-based water monitoring. This one is called OpenET (“ET” refers to evapotranspiration). It will estimate water use in agricultural areas across much of the western United States, and make it available on the web for anyone to see.
